Turmeric has been used for healthcare purposes for thousands of years in traditional medicine systems like Ayurveda and Chinese medicine. The use of turmeric as a medicinal herb can be traced back to ancient India and Southeast Asia, where it was used to treat various ailments such as digestive problems, skin conditions, and wounds.
In traditional Indian medicine, turmeric was considered a “warming” herb that helped balance the body and improve digestion. It was also used as an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agent, applied topically to wounds or ingested to treat internal conditions.
Over time, turmeric spread throughout the world and was adopted by other cultures for its medicinal properties. In the 9th century, Arab physicians began using turmeric for medicinal purposes and it was introduced to Europe through the spice trade.
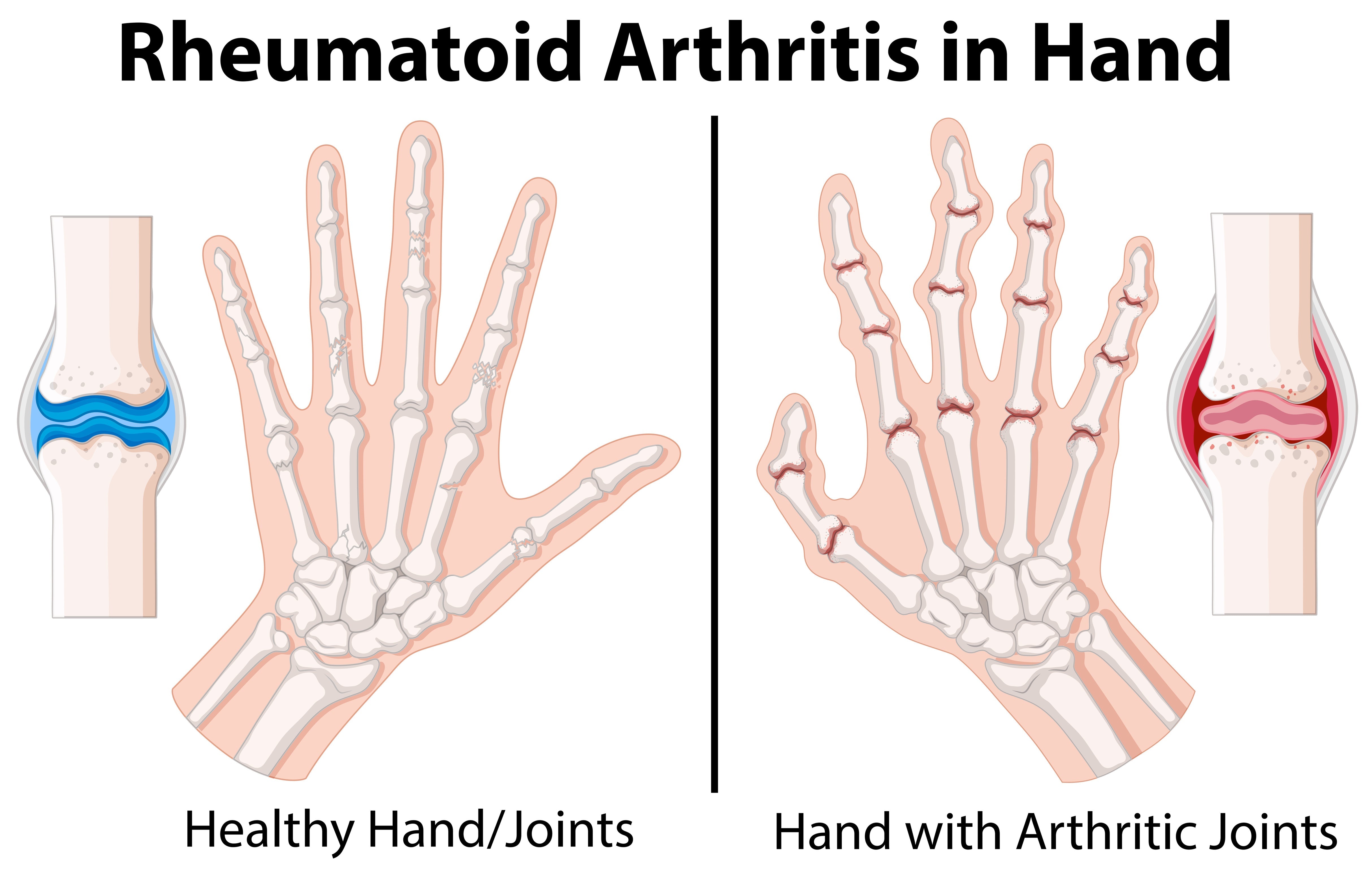
In the past few decades, modern scientific research has confirmed many of the health benefits traditionally attributed to turmeric, including its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Today, turmeric is widely used as a dietary supplement and natural remedy for various health conditions such as arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and depression.