As more people embrace an active lifestyle, the quest for effective ways to enhance recovery and improve performance becomes increasingly important. One natural compound gaining attention in the fitness community is curcumin. Derived from turmeric, curcumin is known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, making it a promising supplement for those dealing with exercise-induced muscle damage (EIMD).
Understanding Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage
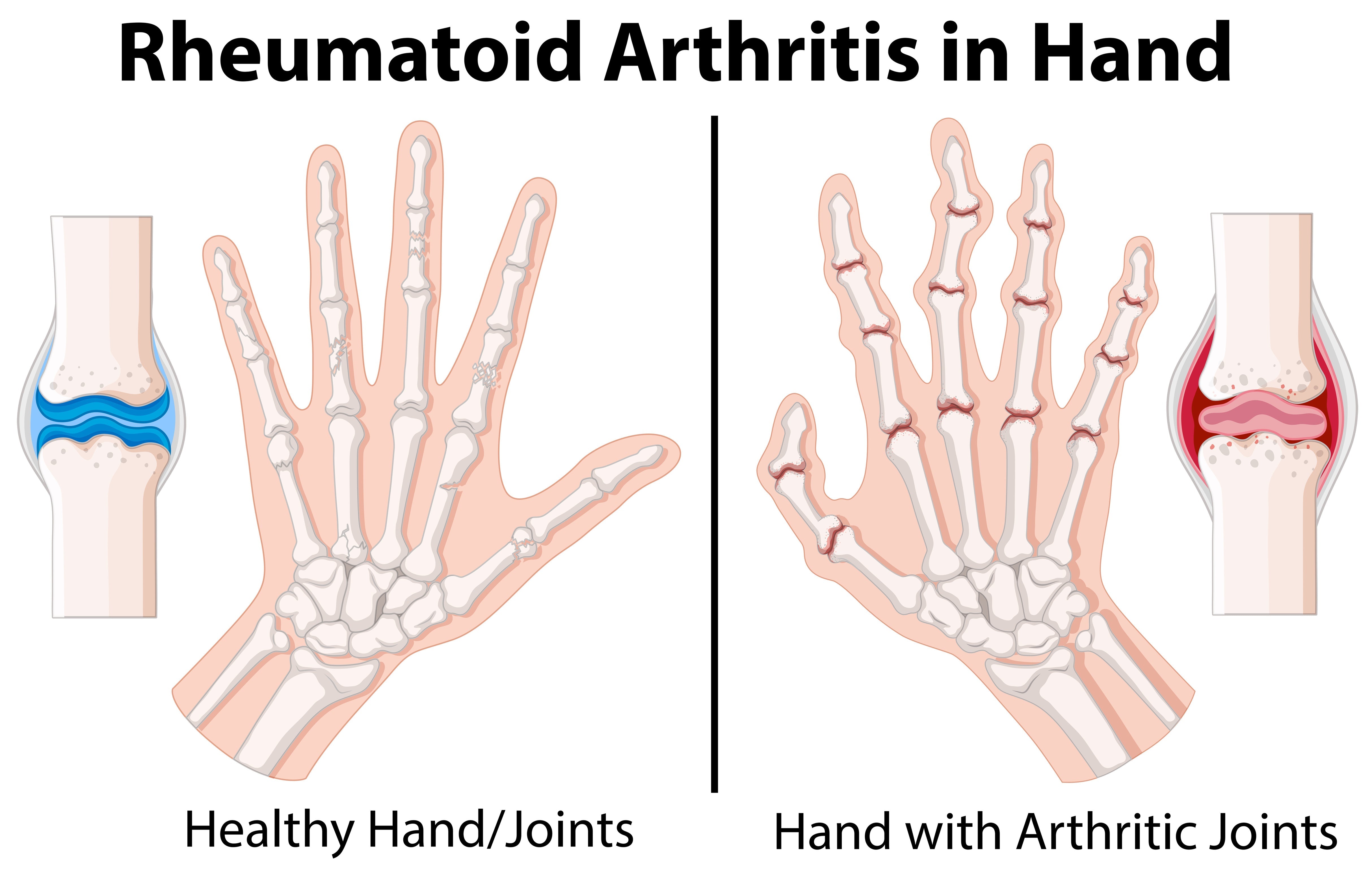
Exercise-induced muscle damage is a common occurrence, especially after intense or unfamiliar physical activity. It manifests as muscle soreness, stiffness, and reduced muscle function, typically peaking 24 to 48 hours post-exercise. This condition, often referred to as delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), results from microscopic tears in muscle fibers, leading to inflammation and oxidative stress.
The Role of Curcumin
Curcumin, the active compound in turmeric, has been used for centuries in traditional medicine. Its potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties have been well-documented in scientific literature. When it comes to EIMD, curcumin's benefits are particularly noteworthy:
1. Reducing Inflammation
Inflammation is a natural response to muscle damage, but excessive inflammation can prolong recovery and cause discomfort. Curcumin inhibits the activity of inflammatory enzymes like cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By modulating the inflammatory response, curcumin can help minimize muscle soreness and accelerate recovery.
2. Combating Oxidative Stress
Intense exercise increases the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to oxidative stress, which can further damage muscle tissue. Curcumin acts as a potent antioxidant, scavenging these harmful free radicals and protecting muscle cells from oxidative damage. This dual action of reducing inflammation and oxidative stress makes curcumin an effective agent in mitigating the effects of EIMD.
3. Enhancing Muscle Repair and Recovery
Beyond reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, curcumin may also promote muscle repair. Studies suggest that curcumin can enhance the proliferation and differentiation of muscle cells, facilitating the regeneration of damaged muscle fibers. This can lead to improved muscle function and quicker recovery times.
4. Improving Performance and Endurance
By aiding in faster recovery and reducing muscle soreness, curcumin can indirectly improve athletic performance. Athletes may experience less downtime due to DOMS, allowing for more consistent and intensive training sessions. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin can help in managing chronic conditions like arthritis, enabling individuals to maintain an active lifestyle with less discomfort.
How to Incorporate Curcumin into Your Routine
To reap the benefits of curcumin, it's important to consider its bioavailability. Curcumin naturally has poor absorption in the body, but this can be improved by:
- Using Curcumin Supplements: Many supplements are formulated with enhanced bioavailability, using technologies like liposomal curcumin, microactive curcumin or curcumin nanoparticles.
- Including in Diet: Adding turmeric to meals, especially with a pinch of black pepper and a fat source (like coconut oil), can increase curcumin uptake.
Conclusion
Curcumin offers a natural and effective way to manage exercise-induced muscle damage, thanks to its powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. By reducing inflammation, combating oxidative stress, and promoting muscle repair, curcumin can help athletes and fitness enthusiasts recover faster and perform better. Incorporating curcumin into your diet or supplement regimen could be a game-changer in your fitness journey.
As always, it's advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications. With the right approach, curcumin can become a valuable ally in achieving your fitness goals and maintaining an active lifestyle.